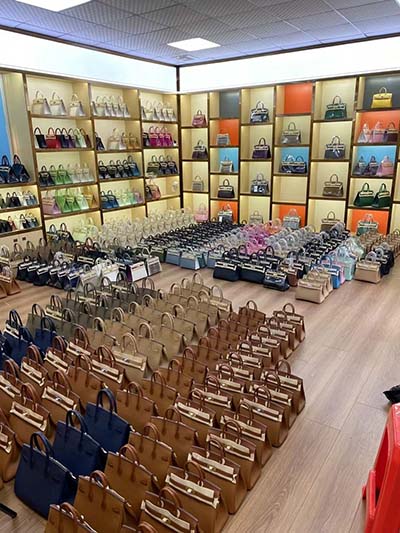
lv wall contraction | Twist Mechanics of the Left Ventricle: lv wall contraction Left ventricular contractility. The primary central abnormality in HF is an impaired left ventricular (LV) contractility or contractile reserve. Patients with an LV ejection fraction (LVEF) less than . The iconic Louis Vuitton Damier and Monogram patterns can be found on many authentic products such as the Alma, Neverfull and Speedy. Yet they’re often imitated by unscrupulous sellers. Here’s a detailed list made to help you identify authentic and fake Louis Vuitton handbags.
0 · Twist Mechanics of the Left Ventricle: Principles and
1 · Twist Mechanics of the Left Ventricle:
2 · The Cardiac Cycle and the Physiological Basis of Left Ventricular
3 · Physiology, Left Ventricular Function
4 · Left ventricular hypertrophy
5 · Left ventricular function: time
6 · Left Ventricular Twist and Torsion
7 · Left Ventricular Structure and Function: Basic Science for Cardiac
8 · Left Ventricle Heart
9 · Heart Left Ventricle Contraction
10 · Heart Left Ventricle Contractility
In this video I'm gonna show you guys how to farm level 40 Joey Wheeler. Just use a Cerberus deck witha few adjustments. Check out our Facebookhttps://www.fa.
The contraction of subepicardial fibers will rotate the apex of the LV in counterclockwise and its base in clockwise direction. Conversely, the contraction of .Left ventricular contraction is characterized by complex deformation of the myocardium, including longitudinal myocardial fiber shortening, radial thickening, circumferential shortening, and left .Left ventricular contractility. The primary central abnormality in HF is an impaired left ventricular (LV) contractility or contractile reserve. Patients with an LV ejection fraction (LVEF) less than .Late in diastole, atrial contraction increases the atrial pressure, producing a second atrial-to-LV pressure gradient that again propels blood into the LV. After atrial systole, as the left atrium .

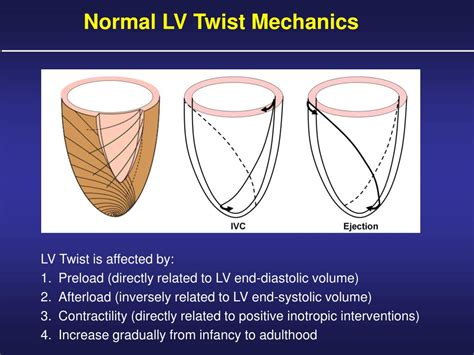
A, Relative rotation of LV base (red curved arrow), and apex (blue curved arrow) during isovolumic contraction, ejection, and isovolumic relaxation and early diastole. B, LV rotational curves for the LV base (red line) and apex . Contractility is best measured by the slope, Emax, of the end-systolic pressure–volume relationship. Ventricular systole is usefully characterized by a time-varying elastance (ΔP/ΔV).In the subendocardium, this torque causes fiber rearrangement such that subendocardial fibers are sheared toward the LV cavity for LV wall thickening, whereas the LV base is pulled toward the apex, shortening the longitudinal . Normal ventricular function requires coordinated electrical activation and contraction. Given the 3-dimensional pattern of ventricular activation and contraction, the assessment of mechanical activation using conventional imaging methods is a complex task.
The left ventricle is an integral part of the cardiovascular system. Left ventricular contraction forces oxygenated blood through the aortic valve to be distributed to the entire body. With such an important role, decreased function caused by injury or maladaptive change can induce disease symptoms. The contraction of subepicardial fibers will rotate the apex of the LV in counterclockwise and its base in clockwise direction. Conversely, the contraction of subendocardial fibers will rotate the LV apex and base in exactly the opposite directions.The left ventricle is conical in shape with an anteroinferiorly projecting apex and is longer with thicker walls than the right ventricle. It is separated from the right ventricle by the interventricular septum, which is concave in shape (i.e. bulges into the right ventricle).Left ventricular contraction is characterized by complex deformation of the myocardium, including longitudinal myocardial fiber shortening, radial thickening, circumferential shortening, and left ventricular twist or torsion.
Twist Mechanics of the Left Ventricle: Principles and
Left ventricular contractility. The primary central abnormality in HF is an impaired left ventricular (LV) contractility or contractile reserve. Patients with an LV ejection fraction (LVEF) less than 50% (or <40% depending on which definition is used) are referred to as having systolic HF or HF with reduced EF (HFrEF).
Late in diastole, atrial contraction increases the atrial pressure, producing a second atrial-to-LV pressure gradient that again propels blood into the LV. After atrial systole, as the left atrium relaxes, its pressure decreases below the LV pressure, causing the mitral valve to begin closing. A, Relative rotation of LV base (red curved arrow), and apex (blue curved arrow) during isovolumic contraction, ejection, and isovolumic relaxation and early diastole. B, LV rotational curves for the LV base (red line) and apex (blue line) from a normal healthy subject.
Contractility is best measured by the slope, Emax, of the end-systolic pressure–volume relationship. Ventricular systole is usefully characterized by a time-varying elastance (ΔP/ΔV).In the subendocardium, this torque causes fiber rearrangement such that subendocardial fibers are sheared toward the LV cavity for LV wall thickening, whereas the LV base is pulled toward the apex, shortening the longitudinal axis of the LV. Normal ventricular function requires coordinated electrical activation and contraction. Given the 3-dimensional pattern of ventricular activation and contraction, the assessment of mechanical activation using conventional imaging methods is a complex task. The left ventricle is an integral part of the cardiovascular system. Left ventricular contraction forces oxygenated blood through the aortic valve to be distributed to the entire body. With such an important role, decreased function caused by injury or maladaptive change can induce disease symptoms.
Twist Mechanics of the Left Ventricle:
The contraction of subepicardial fibers will rotate the apex of the LV in counterclockwise and its base in clockwise direction. Conversely, the contraction of subendocardial fibers will rotate the LV apex and base in exactly the opposite directions.
The left ventricle is conical in shape with an anteroinferiorly projecting apex and is longer with thicker walls than the right ventricle. It is separated from the right ventricle by the interventricular septum, which is concave in shape (i.e. bulges into the right ventricle).Left ventricular contraction is characterized by complex deformation of the myocardium, including longitudinal myocardial fiber shortening, radial thickening, circumferential shortening, and left ventricular twist or torsion.
louis vuitton prices aruba
Left ventricular contractility. The primary central abnormality in HF is an impaired left ventricular (LV) contractility or contractile reserve. Patients with an LV ejection fraction (LVEF) less than 50% (or <40% depending on which definition is used) are referred to as having systolic HF or HF with reduced EF (HFrEF).Late in diastole, atrial contraction increases the atrial pressure, producing a second atrial-to-LV pressure gradient that again propels blood into the LV. After atrial systole, as the left atrium relaxes, its pressure decreases below the LV pressure, causing the mitral valve to begin closing.
A, Relative rotation of LV base (red curved arrow), and apex (blue curved arrow) during isovolumic contraction, ejection, and isovolumic relaxation and early diastole. B, LV rotational curves for the LV base (red line) and apex (blue line) from a normal healthy subject. Contractility is best measured by the slope, Emax, of the end-systolic pressure–volume relationship. Ventricular systole is usefully characterized by a time-varying elastance (ΔP/ΔV).In the subendocardium, this torque causes fiber rearrangement such that subendocardial fibers are sheared toward the LV cavity for LV wall thickening, whereas the LV base is pulled toward the apex, shortening the longitudinal axis of the LV.
The Cardiac Cycle and the Physiological Basis of Left Ventricular
Physiology, Left Ventricular Function
Left ventricular hypertrophy
Left ventricular function: time
Look out for luggage from the Supreme collab and discover accessories here. Shop 100s of vintage styles from our range of pre-owned Louis Vuitton bags on FARFETCH. Discover second hand & used Louis Vuitton bags & get free returns.
lv wall contraction|Twist Mechanics of the Left Ventricle: